I always wondered how Facebook does its ‘in post’ language translation, and now I know.
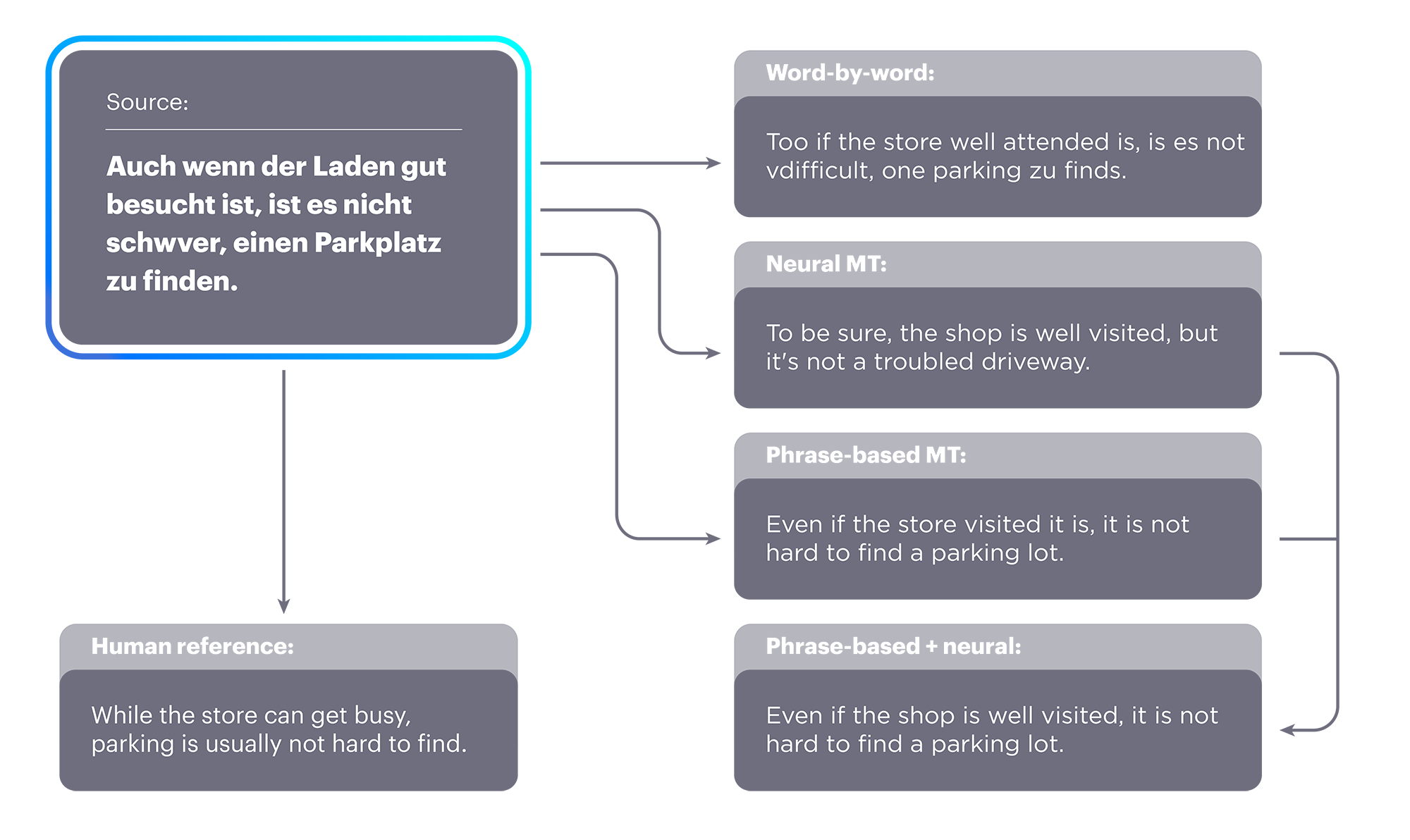
Our new approach provides a dramatic improvement over previous state-of-the-art unsupervised approaches and is equivalent to supervised approaches trained with nearly 100,000 reference translations. To give some idea of the level of advancement, an improvement of 1 BLEU point (a common metric for judging the accuracy of MT) is considered a remarkable achievement in this field; our methods showed an improvement of more than 10 BLEU points.It would appear that this is a multi-step process starting with a word-by-word translation, language modeling, then back translation.
In our research, we identified three steps — word-by-word initialization, language modeling, and back translation — as important principles for unsupervised MT.Then they put it into an 'unsupervised neural model' that did ok and was used for the back translation sentences.
The first one was an unsupervised neural model that was more fluent than word-by-word translations but did not produce translations of the quality we wanted. They were, however, good enough to be used as back-translation sentences. With back translation, this method performed about as well as a supervised model with 100,000 parallel sentences. via F codeAll this reminds me of when Google's machine learning process created it's 'own' interface language for translating languages. Overall, pretty darn cool if you ask me.